
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is a cancer of the lymphatic system, which is part of the immune system.
About 800 people are diagnosed with non-Hodgkin lymphoma each year in Ireland. Lymphoma can occur at any age but it is more common in older people.
There are 2 main types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma: low grade and high grade.
On this page:
What is non-Hodgkin lymphoma?
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is a cancer of your lymphatic system, which is part of the immune system. Read more about the lymphatic system below.
Lymphoma is a type of blood cancer. In lymphoma, the cells that are affected are white blood cells called lymphocytes. They can be B or T lymphocytes. These lymphocytes become abnormal and cancerous. The lymphocytes grow out of control and do not die off as a normal cell would. They collect in the lymphatic system, particularly in your lymph nodes. This causes the lymph nodes to become swollen.
Lymphoma most commonly affects the lymph nodes, but it can start in almost any part of the body, including the spleen, stomach, small bowel, skin, tonsils, thyroid or testicles. Lymphoma cells can also be found in the bone marrow. Bone marrow is the spongy material in the middle of bones. It makes all the different types of white blood cells, including lymphocytes, red blood cells, which carry oxygen from your lungs to other cells in your body and platelets, which help blood to clot and prevent bleeding and bruising.
Lymphoma that grows outside the lymph nodes is called extra-nodal lymphoma. If you have extra-nodal lymphoma, your specialist doctor and nurse can explain this in more detail and what this may mean for your treatment.
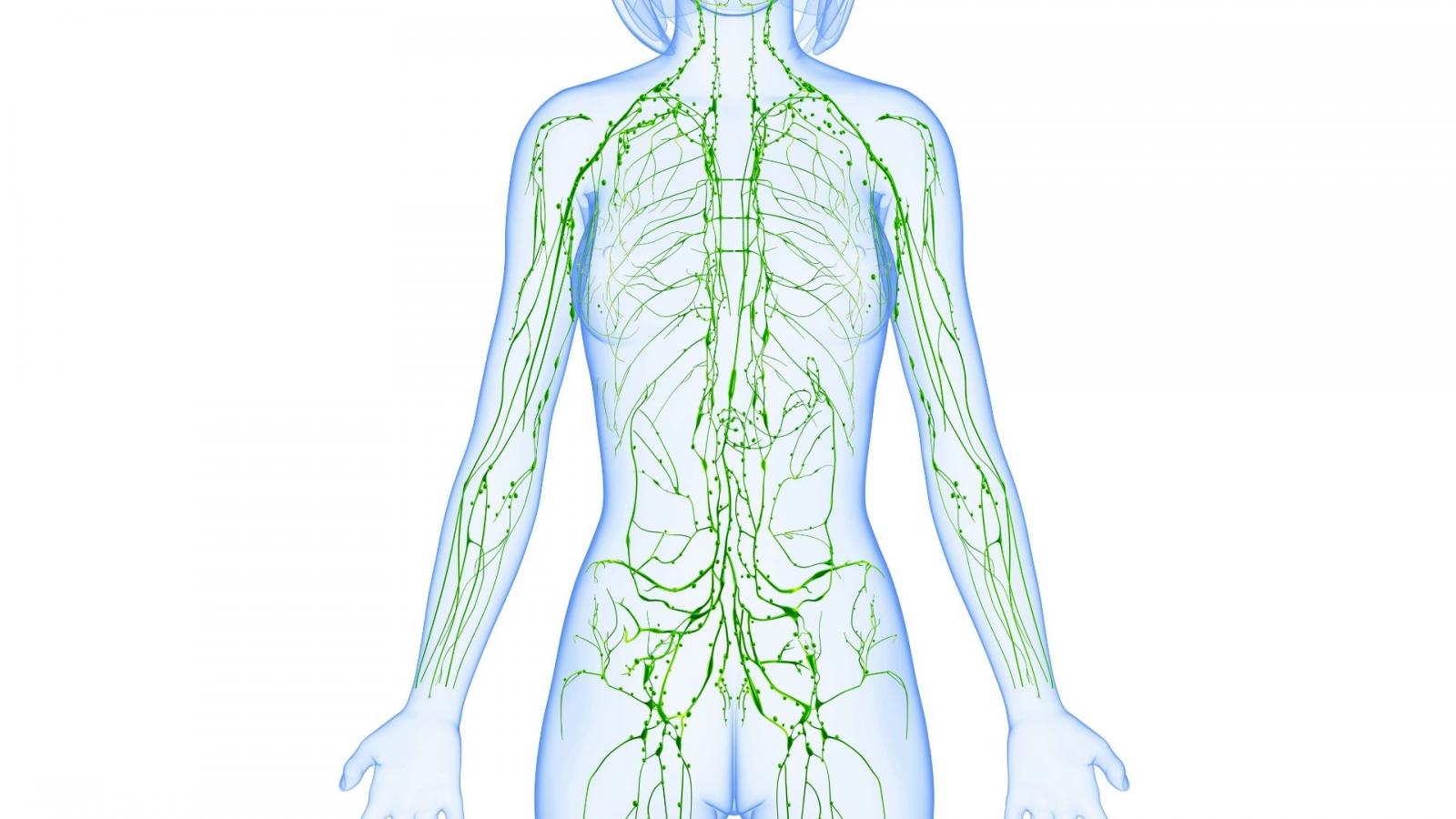
What is the lymphatic system and what does it do?
The lymphatic system is part of the body’s immune system, which helps to protect us from infection and disease.
Parts of the lymphatic system:
- Lymph nodes (or lymph glands): Contain infection-fighting white blood cells called lymphocytes. There are two types of lymphocytes, B-cells and T-cells. Lymph nodes often swell when they are fighting infection, which is a normal, healthy response. Lymph nodes are found mainly in the neck, armpit, groin and tummy. Lymph nodes often swell when they are fighting infection, which is a normal, healthy response. You may only become aware of your lymph nodes if they become swollen or enlarged.
- Lymph vessels: A network of thin tubes that connect lymph nodes and transport excess fluid and waste from body tissues and filter bacteria and viruses.
- The spleen: Helps to filter out damaged cells from the blood stream and also to fight infection.
- Other body organs: Your tonsils, adenoids, thymus and bone marrow.
Sometimes cancer cells spread into lymph nodes or cancer can start in the lymph nodes themselves.
Diagnosing non-Hodgkin lymphoma
More information about non-Hodgkin lymphoma treatment
Treatment for Hodgkin lymphoma includes chemotherapy, radiotherapy, targeted therapies, stem cell transplant and drug treatment.
For more information about treatments for non-Hodgkin lymphoma, visit our treatment page. For information about specific treatments, see the links below.
More information about non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Looking for support?
Our cancer support section contains information and advice on coping with cancer for diagnosed patients and their loved ones.
The Irish Cancer Society uses the most up-to-date cancer statistics from the National Cancer Registry Ireland, available on www.ncri.ie
For more information
Phone
1800 200 700












